RESEARCH
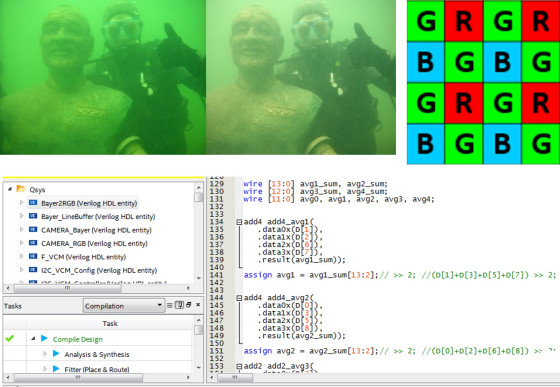
Underwater image enhancement based on FPGA
When light propagates underwater, it is usually affected by water absorption and scattering, resulting in a reduction in the contrast, clarity, and color reproduction of underwater images, resulting in distortion of underwater images. To improve underwater image quality, this study proposes a real-time image enhancement method using RGB light sensors and FPGA. The RGB light sensor is used to measure the color of the waterbody. Based on the measured color of the waterbody, the high-speed computing of the FPGA is applied to enhance the color channels lost due to absorption of the underwater image to achieve real-time enhancement of the underwater image.
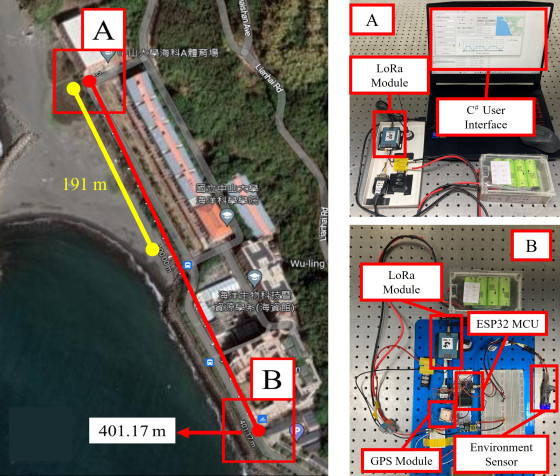
Wireless signal transmission of environmental monitoring
The frequent entry and exit of ships in the port makes it prone to various sources of pollution, and oil spills are one of them. If the oil spill isn't aware immediately after the accident, the oil slick will be affected by wind and waves and increase the range of pollution. This phenomenon not only causes harm to the local environment but also makes it more difficult for rescue units to clean up the environment. This study designs an optical oil slick sensor and combines it with LoRa wireless communication to achieve real-time detection of oil slicks in the port. If multiple points were properly deployed and selected oil spill-prone areas, the oil spill could be determined immediately. It will improve the efficiency of oil slick recovery.
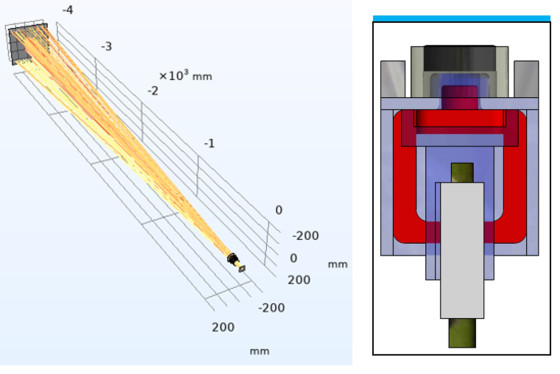
Underwater Distance Measurement
The lens in this study has the characteristic of changing the diopter. After the electromagnetic actuator applies pressure to the optical fluid container, it causes the lens to deform, and then controls the diopter of the lens through currents, so it can be applied to focus at different depths. Through the measurement algorithm, the distance can be calculated and presented.
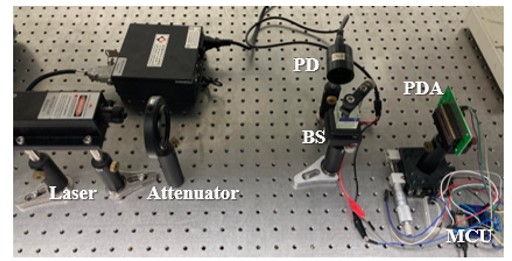
Refractive index measurement of seawater
This study improves the seawater refractive index sensor from M. L. Menn's measurement setup (2011). Due to the variations in the refractive index of seawater, displacements of the measured laser spot are measured by the photoarray to determine the refractive index, and the difference in the refractive index of seawater is related to the salinity.
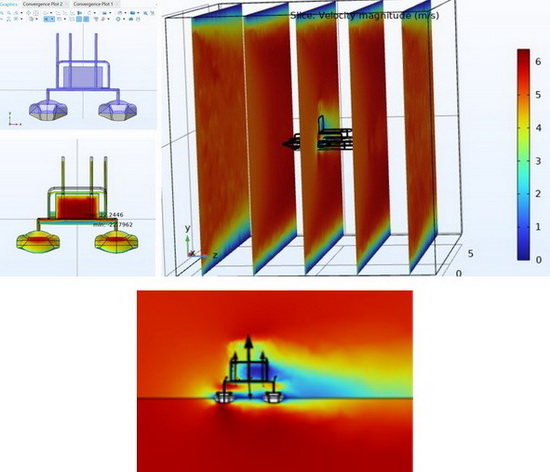
Wind loads simulation in a ship on the sea
Using finite element simulation software to simulate the wind load of the ship on the sea surface. In dynamic positioning applications, the minimum reference thrust requirement could be calculated by the simulation.
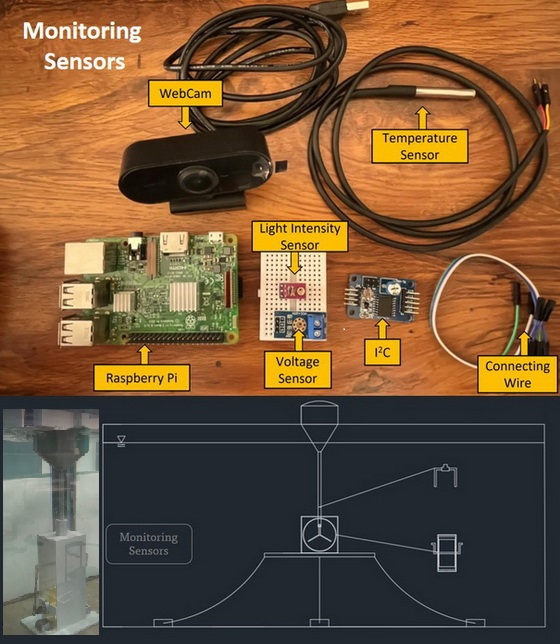
Daylight harvesting and optical fiber transmission system applied to the Sarcodia suiae cultivation
The innovative light- harvester and the optical fiber transmission are applied to the Sarcodia suiae breeding system, which includes a buoy-type platform and a submerged Sarcodia suiae breeding tank. The buoy-type platform is a semi-submersible cylinder. The harvested light is transmitted to the cultivation tank through optical fibers. In addition to optical lighting, the solar panels were also placed on the floating platform to provide LED lighting. By using a proper mechanism, the wave-induced up-down motion of the platform can be easily transferred into a rotational motion that drives the blades inside the cultivation tank and stirs the Sarcodia suiae in the breeding tank, and the Sarcodia suiae can evenly receive the lights. This design may greatly eliminate energy consumption such as cooling water, stirring motor, circulating seawater extraction, etc. The cultivation cost is, therefore, greatly reduced. The monitoring system includes a voltage sensor, light intensity sensor, and temperature sensor, all of them collected by Raspberry Pi.
Shock absorption- floating offshore wind turbine
This study presents the loading of wind and waves on the floating wind turbine analyzed by the comprehensive load analysis software "FAST". Its type is a 5MW offshore floating wind turbine (Semi-Submersible). In addition to the wind and wave conditions, since Taiwan is located in the seismic zone, the seismic force is also considered. The oil tank at the bottom of the fan has different damping effects under wind, wave, and earthquake forces, which can also achieve shock absorption. The two-dimensional numerical calculation model established by the finite difference method is used to analyze the dynamic response of water in oil tanks under the action of external forces such as the wind, waves, and earthquakes.
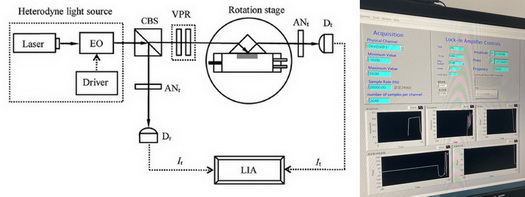
Optical vacuum pressure sensor
This research demonstrates a phase-sensitive total-internal-reflection (TIR) sensing system for measuring vacuum pressure. In the system, linearly polarized light propagates through a specially-designed phase-sensitive TIR apparatus composed of a wave-plate type phase shifter, an isosceles right-angle prism combined with a vacuum cavity, and an analyzer. Under the suitable axis azimuth of the wave plates and the analyzer, it can raise the phase difference of the s- and p- polarization states of the totally-reflected light beam from the TIR apparatus. The raised phase difference is related to the vacuum pressure; therefore, the pressure is easily and accurately determinable by measuring the phase difference variation using the heterodyne phase-detection technique. The experimental results demonstrated the feasibility of this method. Measurement resolution and sensitivity levels superior to 0.4 torr and 0.02°/torr were respectively attainable in the measurement region of 10 torr to 760 torr.
Optical relative humidity sensor
This study presents an optical relative humidity sensor based on the hydrophilic feature of a polyvinyl alcohol film and a phase-enhancement total-internal-reflection heterodyne interferometer. The sensor operation is based on the interaction of a total-internal-reflection evanescent wave with polyvinyl alcohol film- coated on the base of a phase-enhancement total-internal-reflection apparatus. Relative humidity influences the polyvinyl alcohol refractive index, thus bringing a significant variation in the phase difference between the s- and p- polarized states of abeam completely reflected from the total-internal-reflection apparatus. The phase difference variation can be obtained using the heterodyne interferometric technique, and the relative humidity measurement, therefore, is realized. In this study, the sensor produced measurement sensitivity and resolution superior to 0.49。/% RH and 0.5% RH in the range of 30%–75% RH.